Menu
OIC CHECKLIST
Help them give you the whole story
Consider these steps
1

DISCUSS

CLICK TO
REVEAL STEP 1
REVEAL STEP 1
Ask patients about the frequency and consistency of bowel movements and associated symptoms
Record frequency of bowel movements during treatment
2

CLINICAL
ASSESSMENT

CLICK TO
REVEAL STEP 2
REVEAL STEP 2
Talk with your patient within the first week of starting opioid therapy to see if they are experiencing side effects
Use the Bowel Function Index, a clinically validated tool to measure relevant changes in constipation1
You can also use theas a visual tool to aid your discussion2
A thorough clinical assessment is key for the diagnosis of OIC in patients with cancer, with particular focus on the baseline bowel habit and any changes that may occur following introduction of an opioid2
- The Rome IV criteria have been shown to be approximately 82% accurate for the diagnosis of OIC1
- Simply asking, “Are you constipated?” has been shown to be inadequate in consistently diagnosing OIC1
3

REVIEW
MEDICATION

CLICK TO
REVEAL STEP 3
REVEAL STEP 3
Consider the use of a laxative agent when treating OIC
- Traditional laxatives include osmotic, stimulants, stool softeners, and lubricants3
- Bulk-forming agents should be avoided in the management of OIC3
4

CONSIDER
MOVENTIG

CLICK TO
REVEAL STEP 4
REVEAL STEP 4
If the response to a laxative is inadequate, consider MOVENTIG4

OIC, opioid-induced constipation.
See why a change in treatment approach may be needed.
Consider MOVENTIG 
References 1. Davies A, Leach C, Butler C, et al. Opioid-induced constipation in patients with cancer: a “real-world,” multicentre, observational study of diagnostic criteria and clinical features. Pain. 2021;162(1):309-318. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002024 2. Farmer AD, Drewes AM, Chiarioni G, et al. Pathophysiology and management of opioid-induced constipation: European expert consensus statement. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2019;7(1):7-20. doi:10.1177/2050640618818305 3. Crockett SD, Greer KB, Heidelbaugh JJ, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on the Medical Management of Opioid-Induced Constipation. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(1):218-226. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.016 4. MOVENTIG Summary of Product Characteristics. Accessed May 2022. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/30483/smpc
Bristol Stool Form scale1
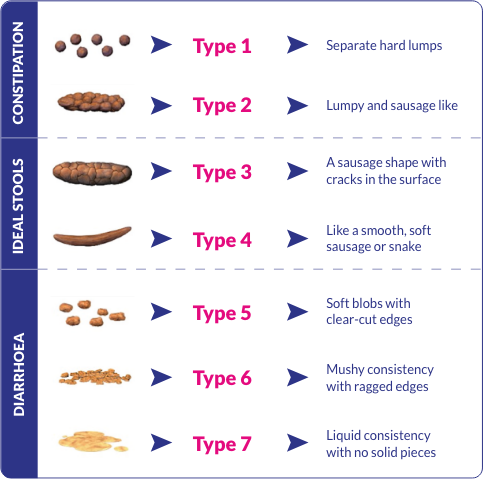
Reference 1. Lewis SJ, Heaton KW. Stool Form Scale as a useful guide to intestinal
transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32(9):920-924. doi:10.3109/00365529709011203
VIEW PRESCRIBING INFORMATION 

PRESCRIBING INFORMATION (prepared August 2021)
Moventig® (naloxegol oxalate) 12.5mg and 25mg film-coated tablets
Consult Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) before prescribing.
Indication: Opioid-induced constipation (OIC) in adult patients who have had an inadequate response to laxative(s) (concurrent OIC symptoms of at least moderate severity while taking at least one laxative class for a minimum of four days during the previous 2 weeks).
Dosage and administration: Recommended 25 mg once daily. Take on empty stomach at least 30 minutes prior to first meal of day or 2 hours after first meal of day. Crushed tablets can be mixed with water (120ml) and drunk immediately or administered via a nasogastric tube (CH8 or greater). Renal impairment: Moderate or severe renal impairment starting dose 12.5mg. Discontinue if side effects impact tolerability. Increase to 25mg if well tolerated. Hepatic impairment: Use in severe hepatic impairment not recommended. Moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors: Starting dose 12.5mg, can be increased to 25mg if well tolerated. Paediatric population (<18 years): Safety and efficacy not yet established.
Adverse effects: Consult SmPC for full list of side effects. Very Common: Abdominal pain, diarrhoea. Common: Nasopharyngitis, headache, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis. Uncommon: Opioid withdrawal syndrome. Not known: Hypersensitivity, Gastrointestinalperforation.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to active substance or any of the excipients or any other opioid antagonist. Patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal (GI) obstruction or patients at increased risk of recurrent obstruction. Patients with underlying cancer who are at heightened risk of GI perforation, such as those with underlying malignancies of gastrointestinal tract or peritoneum, recurrent or advanced ovarian cancer or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor treatment. Concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Warnings and precautions: Cases of gastrointestinal perforation have been reported in the post-marketing setting, including fatal cases when naloxegol was used in patients who were at an increased risk of gastrointestinal (GI) perforation. Naloxegol must not be used in patients with known or suspected gastrointestinal obstruction or in patients at increased risk of recurrent obstruction. Use with caution in patients with any condition which might result in impaired integrity of the gastrointestinal tract wall. Advise patients to discontinue therapy and promptly report if unusually severe or persistent abdominal pain develops. Use with caution in patients with clinically important disruptions to the blood brain barrier and observe for potential CNS effects. Discontinue if interference with opioid-mediated analgesia or opioid withdrawal syndrome occurs. Use with caution in patients taking methadone. If opioid withdrawal syndrome is suspected the patient should discontinue Moventig and contact their physician. Use with caution in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction, symptomatic congestive heart failure, overt cardiovascular (CV) disease or with a QT interval of ≥500msec. Use with caution in OIC patients with cancer-related pain. Use of naloxegol with another opioid antagonist (e.g. naltrexone, naloxone) should be avoided.
Use in pregnancy and lactation: Not recommended.
Legal category: POM.
Marketing Authorisation numbers: Moventig 12.5mg and 25mg tablets (ROI: EU/1/14/962/001-011),(GB: PL GB 50262/004&5)
Further information available on request from the Marketing Authorisation holder: Kyowa Kirin Holdings B.V., Bloemlaan 2, 2132NP Hoofddorp, The Netherlands.
For the United Kingdom:
NHS cost: Moventig 12.5mg, 30 tablets, £55.20; Moventig 25mg, 30 tablets, £55.20.
NHS cost: Moventig 12.5mg, 30 tablets, £55.20; Moventig 25mg, 30 tablets, £55.20.
Adverse Events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard. Adverse Events should also be reported to Kyowa Kirin Ltd. on +44 (0)1896 664000, email medinfo@kyowakirin.com
For the Republic of Ireland:
Adverse Events should be reported. Information about adverse event reporting can be found at www.hpra.ie. Adverse Events should also be reported to Kyowa Kirin Ltd. on +44 (0)1896 664000, email medinfo@kyowakirin.com
This program is best viewed on a device with a higher screen resolution. Some content may not be optimally presented.